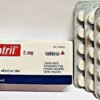
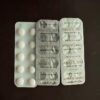
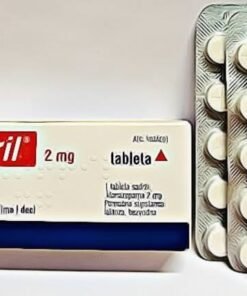
Clonazepam 2mg
$245.00 – $425.00
Fast Us to Us Delivery
No Prescription Needed
SKU: RXP06
Category: Anxiety Medications
| Quantity | 30, 60, 90, 180 |
|---|
Be the first to review “Clonazepam 2mg” Cancel reply
Related products
Anxiety Medications
$275.00 – $425.00
Anxiety Medications
$100.00 – $375.00
Anxiety Medications
$275.00 – $425.00
Anxiety Medications
$100.00 – $375.00
Anxiety Medications
$150.00 – $425.00
Anxiety Medications
$100.00 – $375.00
Anxiety Medications
$80.00 – $325.00
Anxiety Medications
$199.00



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.